Women’s Health
Recently postpartum? Feel pressure in the vaginal region? Have pain with intercourse? Have issues with incontinence? This could be urinary or even fecal incontinence. A woman’s pelvic floor muscles carry the load of our day-to-day lives but increased stress from childbirth or weakening with age can result in a variety of pelvic floor dysfunctions. For generations, women have believed these symptoms to be a “normal” part of being a woman; these symptoms are NOT normal and CAN be addressed without surgery. A Pelvic Physical Therapist can help in all areas related to Women’s Health from pre-natal to post-menopause. We are here to help women of all ages to return to their active lives and improve their quality of life.
WHAT TO EXPECT:
90 minute one-on-one assessment with a licensed physical therapist who specializes in pelvic floor physical therapy
A musculoskeletal examination including back, hip, and abdominal screenings as well as both external and internal assessment of the pelvic floor muscles
Development of strengthening or down training program, dependent on your presentation
Strengthening – Based on the weak muscles, and this includes pelvic floor, hips, as well as abdominal musculature, strengthening exercises incorporated with functional activities that you perform on a daily basis
Down Training – Based on the muscles with increased tension or tenderness, performance of hands-on myofascial release, stretching, and breathing techniques to reduce muscle tension and nervous system stress
Education regarding appropriate toileting hygiene and posture, bladder training, and dietary alterations as necessary
Functional training to avoid exacerbating symptoms, improve performance of everyday activities, and reduce changes of injury
Including lifting, squatting, reaching, bending, and balancing activities
Areas of Specialty:
Urinary urgency, frequency, and incontinence
Fecal incontinence
Constipation
Dyspareunia (pain with intercourse)
Pelvic Organ Prolapse
Pelvic pain
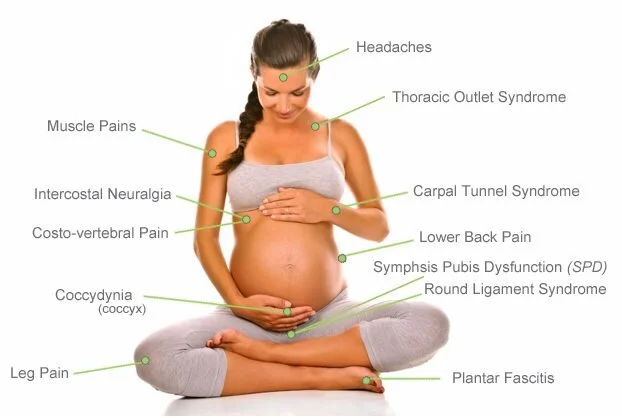
Pregnancy/postpartum care
Abdominal pain
Symphysis Pubis Dysfunction
Sacroiliac Joint Dysfunction
Diastasis Recti